Diagnosis and Prevention for Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid disease can be any one of the conditions that affect the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland produces a hormone known as thyroxine which regulates the metabolic functions of the body and aids in performing normal bodily functions. An imbalance in thyroid hormone levels can cause several complications.
Thyroid hormone deficiency causes hypothyroidism, and elevated levels of thyroid hormones cause hyperthyroidism. The thyroid gland may also develop cancer, which is a potentially lethal disease. Thyroid disease and its causes, symptoms, and types are a subject of medical research. With proper medical care, these conditions can be successfully treated.
How is thyroid disease diagnosed?
Depending on which thyroid disease you are affected by, the doctor will recommend tests and screening procedures based on clinical examination and physical tests. Some of the common diagnostic procedures are:
- Physical examination
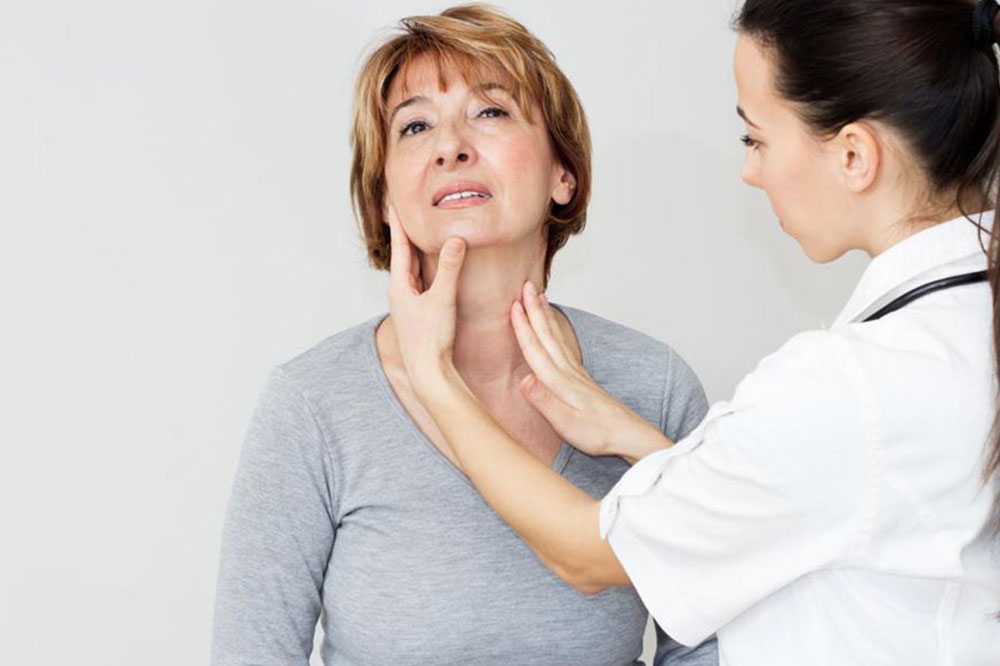
This involves the physician checking your neck for lumps or abnormalities in the thyroid structure. Your reflexes may also be tested since slow reaction speed often indicates hypothyroidism. Your blood pressure and heart rates may be measured as a part of the standard procedure. If you are visibly overweight, the doctor might measure your weight and discuss diet. Other factors that are examined include body temperature, hair volume, and texture, skin texture, eyes, among others. A physical examination will often present the doctor with a rough idea about thyroid disease and its causes, symptoms, and types.
- Blood sample tests
A sample of your blood may be taken and tested for the following: Thyroxine, Thyroglobulin, Thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin, Triiodothyronine, Antithyroid, and Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies.
- Biopsy
This involves the extraction of a small part of your thyroid tissue. This is usually done to test for cancerous cells.
- Screening and Imaging
Techniques such as MRI scans are used to determine the shape and size of the thyroid gland to detect irregularities. CT scan may be used to detect the presence of goiter or nodules in the thyroid.
- Radioactive iodine uptake (RAIU) test
In this procedure, radioactive iodine is introduced into the body and a gamma probe is used to measure how much iodine your thyroid gland has absorbed.
Your endocrinologist is well-versed in thyroid disease and its causes, symptoms, and types, and will recommend treatment procedures based on the results of the diagnostic tests.
Preventing thyroid cancer
Here are some of the ways you can prevent thyroid diseases.
- Quit smoking
Smoking cigarettes can cause an imbalance in your iodine levels, and cause your body to produce more thyroxine hormone.
- Wear a thyroid collar
A thyroid collar can protect you from radiation in the case of a nuclear disaster.
- Limit your intake of soy products
Individuals with hypothyroidism often have to take thyroid supplements such as levothyroxine. But consuming too many soy products can cause problems with the absorption of levothyroxine.
- Switch to a Mediterranean diet
Some doctors recommend following a Mediterranean diet to control inflammation of the intestinal linings which often lead to thyroid disease. A Mediterranean diet includes varieties of fruits, vegetables, as well as fishes such as mackerel, salmon, and herring.
- Selenium supplements
Selenium supplements are often used to treat hypothyroidism.
Thyroid disease can be painful and last for a long time, but following the above mentioned preventive methods and the advice from your doctor, you can survive it.